Introduction
Nodal is a powerful open-source library for graph layout. It enables you to start building beautiful graphs immediately, or configure your own algorithm for any use case.
Why?
There are plenty of graph layout libraries out there, why build another one? That's what we thought too when we first started working on our graph-heavy a project: one that required visualizing complex software structures like dependencies and computation graphs. But as we'd learn soon enough, there are many problems with existing libraries:
- Simple layouts only. Force-directed or single-direction DAG? No problem. Anything more complicated, like a multi-direction flowchart? Good luck.
- Weird node/edge model. Nodes, groups, leaves, edges, hierarchical edges? Often the abstractions introduce a lot of unnecessary complexity that the user has to shoulder.
- Monolithic algorithms. Beyond the configuration options provided, there's no way to modify parts of the algorithm or reuse parts of its code.
- Hard to tune aesthetics. Want edges that only go at octilinear angles, like a metro map? You better hope the library developer wrote a layout for it. There's no way to modularly tweak aesthetics.
- Buggy implementation. Enough said.
- Costly. Sorry, we're not going to pay hundreds or thousands of dollars to use your closed-source software.
Philosophy
Composable. Nodal allows you to build graph layouts by assembling small, predictable pieces (like points, forces, and constraints) into more complex structures and behaviors.
Hackable. Nodal is designed with an appreciation of the diversity of graph layout needs. Its elegant, well-documented abstractions are easy to extend or replace for domain-specific applications.
Intuitive. Nodal is based on gradient-descent rather than the inscrutable algorithms of traditional layout. This allows you to leverage physical and geometric intuitions while tuning your graphs.
Features
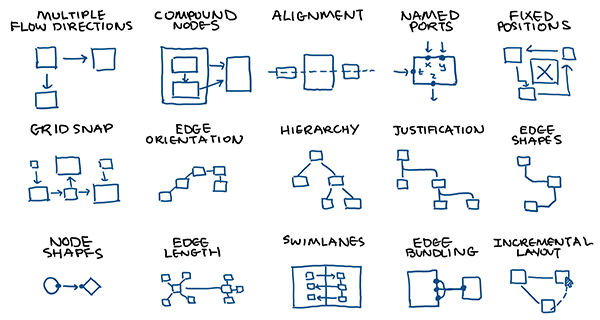
For graph designers:
- Compound nodes
- Different shapes
- Named ports
- Edge angle snap
- Multidirectional flow
- Non-overlap constraints
- Constraints, e.g. alignment, distance
- Animation/interaction hooks
For algorithm builders:
- Small, composable abstractions.
- Layered architecture.
- Elegant, well-documented code.
- Open-source with MIT License.