Architecture
While the API will provide you with the ground-truth documentation about all the abstractions in the library, it's useful to understand the big picture of how everything fits together.
Nodal is built with a 2-level architecture:
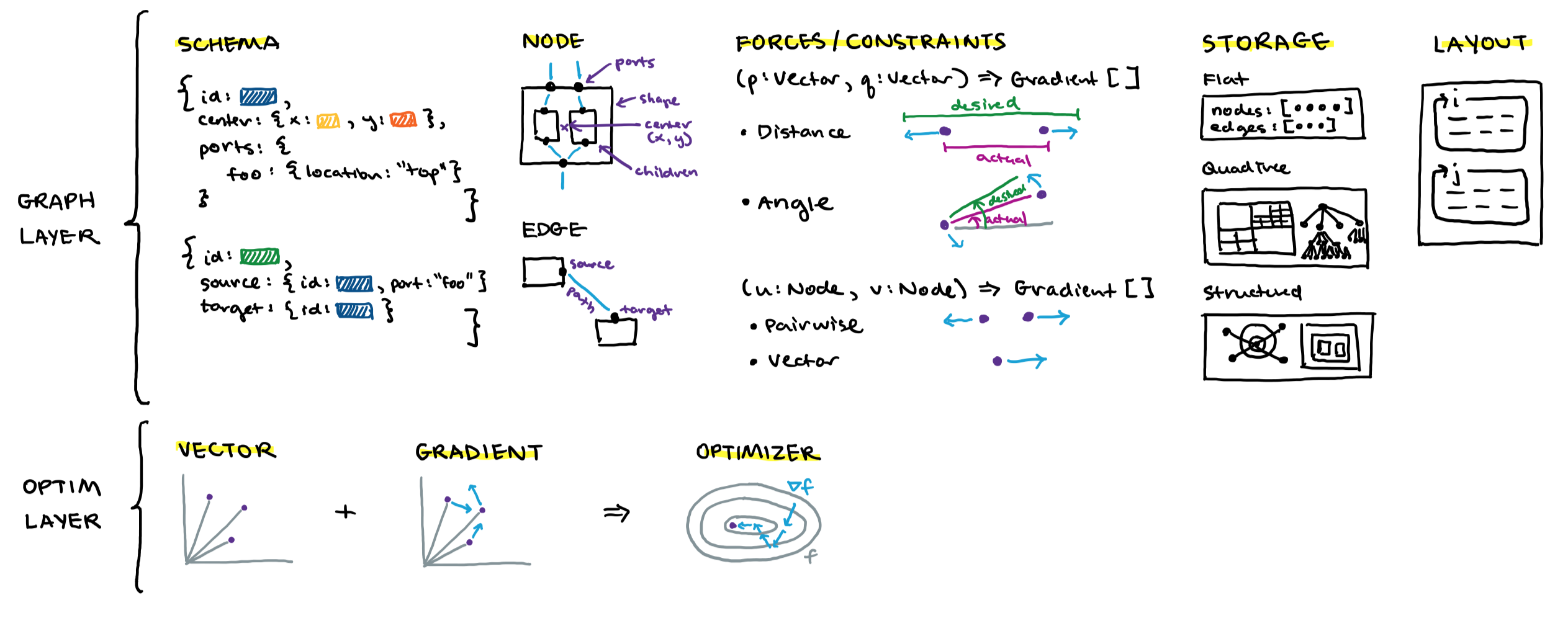
Low-level optim layer
Low-level manipulation of Vectors with Gradients. An Optimizer provides a scheme for adjusting the learning rate multiplier on the gradient. We implemented a constant rate (BasicOptimizer) and adaptive (TrustRegionOptimizer) version, but also think it would be interesting to port some of the ideas from the ML field, e.g. RMSPropOptimizer, AdamOptimizer.
High-level graph layer
Higher-level constructs like Node and Edge (produced from lightweight NodeSchema and EdgeSchema) are just collections of Vectors. Constraints and forces can be exerted on the Vectors through functions that generate Gradients. The entire graph is stored in a Storage which may have different features including performant spatial lookup of elements and complex manipulation/traversal of the graph structure. A developer writes a Layout, which is a graph layout procedure, e.g. i iterations of force application, then j iteractions of constrain projection, repeated for N steps.